Karlodinium
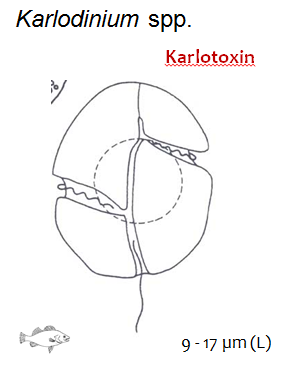
Notes: target, unarmored dinoflagellate, 10 spp., worldwide, toxin, small 9-17um. 4
9-17 µm(L)
Description 4
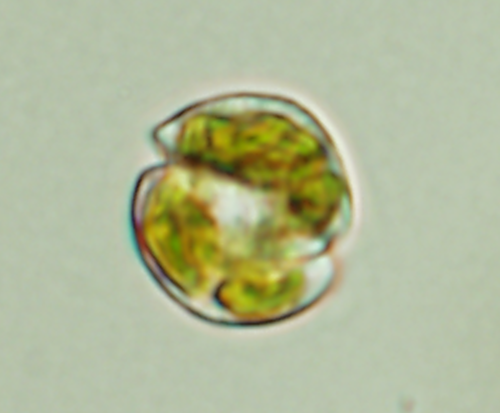
Karlodinium veneficum cells are quite small ranging from 7-14 micrometers in width and 9-18 micrometers in length. The structure of Karlodinium veneficum contains approximately four irregular shaped golden brown chloroplasts that contain many pyrenoids and a centrally located nucleus (4). Karlodinium veneficum also has one or two flagella that are located in opposites directions of each other (2). Along the anterior end of the cell there is a shallow sulcus (a depression or fissure). Karlodinium veneficum is a relatively small microorganism so it is overlooked quite often.
Karlodinium veneficum is structurally similar to Karlodinium veneficum in the sense that both microbes contain flagella and contain the same type of pyrenoids within the chloroplasts. They differ in respect to the color of the chloroplasts, which in K. armiger are a yellow-green color, and also in the length of the apical groove (2).
The cells of Karlodinium veneficum reproduce asexually through binary fission, but it is suggested that an individual cell will soon die out due to environment around it (4).
HAB implications 4
Karlodinium veneficumproduces three harmful karlotoxins called Tx1, Tx2 and Tx3. These karlotoxins have been known to cause harmful algae blooms across the world and may be the result of some recent fish kills along the Chesapeake Bay and a few other places. These karlotoxins have the ability to slow the mobility of other organisms, including fish, in order for K. veneficum to obtain necessary nutrients for food (4). The release of these karlotoxins has been known to contribute to survival strategies of K. veneficum that involve the capturing of prey (4). Tx1 has been found to be more toxic than Tx2 and Tx3, but the functions of all three karlotoxins are similar.
Sources and Credits
- (c) FWC Fish and Wildlife Research Institute, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-ND), https://www.flickr.com/photos/myfwc/5808219516/
- (c) FWC Fish and Wildlife Research Institute, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-ND), https://www.flickr.com/photos/myfwc/8678782150/
- (c) GTM NERR, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC), https://www.flickr.com/photos/gtmnerr/24567583836/
- (c) GTMResearchReserve, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA)
More Info
iNat Map
| Category name | Dinoflagellate |
|---|