Eurasian Magpie
Pica picaSummary 7
The Eurasian Magpie, European Magpie, or Common Magpie (Pica pica) is a resident breeding bird throughout Europe, much of Asia and northwest Africa. It is one of several birds in the crow family named as magpies, and belongs to the Holarctic radiation of "monochrome" magpies. In Europe, "Magpie" is used by English speakers as a synonym for the European Magpie; it is the only magpie in Europe outside the Iberian Peninsula.
National distribution 8
United States
Origin: Unknown/UndeterminedRegularity: Regularly occurring
Currently: Unknown/Undetermined
Confidence: Confident
Physical description 9
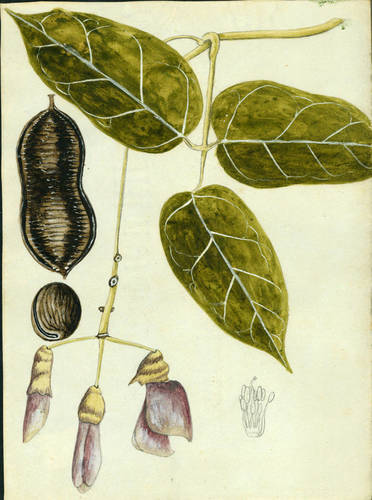
Perennial, Shrubs, Vines, twining, climbing, Woody throughout, Nodules present, Stems greater than 2 m tall, Plants turning black on drying, Stems solid, Stems or young twigs glabrous or sparsely glabrate, Leaves alternate, Leaves petiolate, Stipules inconspicuous, absent, or caducous, Stipules deciduous, Leaves compound, Leaves pinnately 3-foliolate, Leaves odd pinnate, Leaf or leaflet margins entire, Leaflets opposite, Stipels present at base of leaflets, Leaflets 3, Leaves glabrous or nearly so, Inflorescences racemes, Inflorescence axillary, Inflorescence or flowers lax, declined or pendulous, Bracts conspicuously present, Bracteoles present, Flowers zygomorphic, Calyx 2-lipped or 2-lobed, Calyx hairy, Petals separate, Corolla papilionaceous, Petals clawed, Petals greenish yellow, Petals blue, lavander to purple, or violet, Petals bicolored or with red, purple or yellow streaks or spots, Banner petal suborbicular, broadly rounded, Banner petal auriculate, Wing petals narrow, oblanceolate to oblong, Wing petals auriculate, Wing petals incurved, Wing tips obtuse or rounded, Keel abruptly curved, or spirally coiled, Stamens 9-10, Stamens or anthers dimorphic, alternating large and small, Stamens diadelphous, 9 united, 1 free, Filaments glabrous, Style terete, Fruit a legume, Fruit unilocular, Fruit freely dehiscent, Fruit elongate, straight, Fruit oblong or ellipsoidal, Fruit exserted from calyx, Fruit internally septate between the seeds, Fruit hairy, Fruit 2-seeded, Fruit 3-10 seeded, Seeds ovoid to rounded in outline, Seed surface smooth, Seeds olive, brown, or black.
Diagnostic description 10
Mucuna urens (L.) Dc., Prodr. 2: 405. 1825.
Basionym: Dolichos urens L.
Synonym: Mucuna altissima (Jacq.) Dc.
Woody vine, twining, attainig 30 m in length. Stems cylindrical, glabrous, smooth, that turn blackish on drying, attaining up to 10 cm in diameter at the base and producing a watery sap with a pink color. Leaves alternate, trifoliolate, usually pendulous: leaflets coriaceous, glabrous, 7-14 × 4.5-7 cm, the margins entire, upper surface dark green, shiny, glabrous; lower surface light green (purple on juvenile leaflets), shiny, glabrous, with prominent puberulent venation; terminal leaflet elliptical or oblong, the apex acuminate, the base rounded; the lateral leaflets asymmetrical, elliptic-lanceolate, the apex acuminate, the base unequal, truncate-obtuse; petiolules slightly thickened, 5-6 mm long, glabrous or puberulent; stipels absent; petioles 4-9 cm long, striate, thickened at the base; stipules deciduous. Inflorescences of pendulous pseudoracemes; peduncles 1-1.5 m in length. Calyx 1.3-1.7 cm long, ferruginous-pubescent, with one of the sepals longer than the rest; pedicel ca. 2 cm long, ferruginous-pubescent; corolla blue-violet or cardinal red, the standard 3-4 cm long, the wings violet-pink, the keel yellowish, shorter than the wings. Legume woody, more or less oblong, flattened, 12-23 × 5-6 cm, the apex with a long point, the valves with prominent venation, like transverse ribs, which join at the ventral margin to form a sinuate projection, covered with rigid, rust-colored hairs, which separate with great facility and produce a sharp pain on contact. Seeds ca. 3.5 cm wide, circular, hard, brown with a black hilum along more than ¾ of the circumference.
Phenology: Collected in flower from October to April and in fruit in February.
Status: Native, locally common.
Selected Specimens Examined: Acevedo-Rdgz., P. 269; 7799; 9405; 10200; Axelrod, F. 9325; Sintenis, P. 4785; 5041.
Sources and Credits
- (c) Kari Pihlaviita, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC), http://www.flickr.com/photos/42267636@N08/7177173468
- (c) MAPR, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-SA), https://collections.nmnh.si.edu/services/media.php?env=botany&irn=10223323
- (c) Forest & Kim Starr, some rights reserved (CC BY), https://www.biolib.cz/IMG/GAL/50985.jpg
- (c) Acevedo, P., some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-SA), https://collections.nmnh.si.edu/services/media.php?env=botany&irn=10648947
- (c) Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History, Department of Botany, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-SA), https://collections.nmnh.si.edu/services/media.php?env=botany&irn=10349938
- (c) Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History, Department of Botany, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-SA), https://collections.nmnh.si.edu/services/media.php?env=botany&irn=10351488
- (c) Wikipedia, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pica_pica
- (c) NatureServe, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC), http://eol.org/data_objects/29015919
- (c) Dr. David Bogler, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-SA), http://eol.org/data_objects/6657369
- (c) Pedro Acevedo-Rodríguez, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-SA), http://eol.org/data_objects/28435379