White Stork
Ciconia ciconiaDescription 4
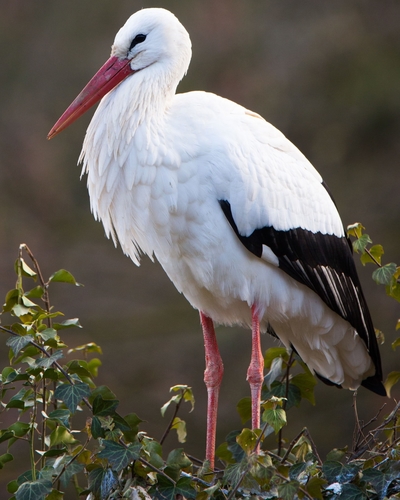
The white stork is a large bird. It has a length of 100–115 cm (39–45 in), and a standing height of 100–125 cm (39–49 in). The wingspan is 155–215 cm (61–85 in) and its weight is 2.3–4.5 kg (5.1–9.9 lb). Like all storks, it has long legs, a long neck and a long straight pointed beak. The sexes are identical in appearance, except that males are larger than females on average. The plumage is mainly white with black flight feathers and wing coverts; the black is caused by the pigment melanin. The breast feathers are long and shaggy forming a ruff which is used in some courtship displays. The irises are dull brown or grey, and the peri-orbital skin is black. The adult has a bright red beak and red legs, the colouration of which is derived from carotenoids in the diet. In parts of Spain, studies have shown that the pigment is based on astaxanthin obtained from an introduced species of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) and the bright red beak colours show up even in nestlings, in contrast to the duller beaks of young white storks elsewhere.
As with other storks, the wings are long and broad enabling the bird to soar. In flapping flight its wingbeats are slow and regular. It flies with its neck stretched forward and with its long legs extended well beyond the end of its short tail. It walks at a slow and steady pace with its neck upstretched. In contrast, it often hunches its head between its shoulders when resting. Moulting has not been extensively studied, but appears to take place throughout the year, with the primary flight feathers replaced over the breeding season.
Upon hatching, the young white stork is partly covered with short, sparse, whitish down feathers. This early down is replaced about a week later with a denser coat of woolly white down. By three weeks, the young bird acquires black scapulars and flight feathers. On hatching the chick has pinkish legs, which turn to greyish-black as it ages. Its beak is black with a brownish tip. By the time it fledges, the juvenile bird's plumage is similar to that of the adult, though its black feathers are often tinged with brown, and its beak and legs are a duller brownish-red or orange. The beak is typically orange or red with a darker tip. The bills gain the adults' red colour the following summer, although the black tips persist in some individuals. Young storks adopt adult plumage by their second summer.
Within its range the white stork is distinctive when seen on the ground. The winter range of C. c. asiatica overlaps that of the Asian openbill, which has similar plumage but a different bill shape. When seen at a distance in flight, the white stork can be confused with several other species with similar underwing patterns, such as the yellow-billed stork, great white pelican and Egyptian vulture. The yellow-billed stork is identified by its black tail and a longer, slightly curved, yellow beak. The white stork also tends to be larger than the yellow-billed stork. The great white pelican has short legs which do not extend beyond its tail, and it flies with its neck retracted, keeping its head near to its stocky body, giving it a different flight profile. Pelicans also behave differently, soaring in orderly, synchronised flocks rather than in disorganised groups of individuals as the white stork does. The Egyptian vulture is much smaller, with a long wedge-shaped tail, shorter legs and a small yellow-tinged head on a short neck. The common crane, which can also look black and white in strong light, shows longer legs and a longer neck in flight.
Cite error: There are tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the <a
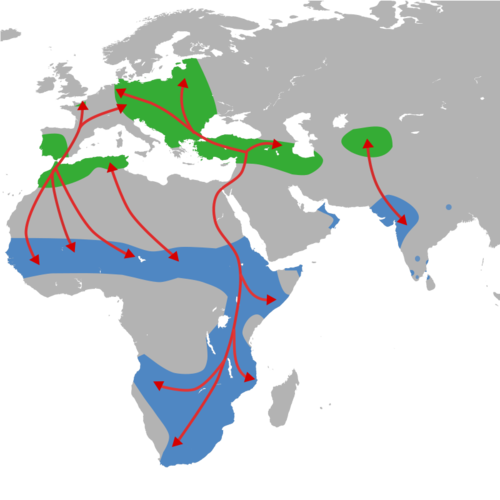
Distribution of Merops apiaster (Photo 11) 5
Green : Breeding range
Blue : Winter range
Red lines : Residental range
Sources and Credits
- (c) Aleksandar, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), uploaded by Aleksandar
- (c) Joachim S. Müller, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-SA), https://www.flickr.com/photos/joachim_s_mueller/34779942405/
- (c) Klaus Rassinger, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ciconia_nigra_MWNH_0881.JPG
- Adapted by Aleksandar from a work by (c) Wikipedia, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_stork
- (c) Aleksandar, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA)
More Info
iNat Map
| Color | black, red, white |
|---|---|
| Region | Banat, Bačka, Južno Pomoravlje, Podrinje i Posavina, Rasina i Toplica, Raška, Srem, Timok i Braničevo, Šopluk, Šumadija |