European polecat
Mustela putoriusDescription 5
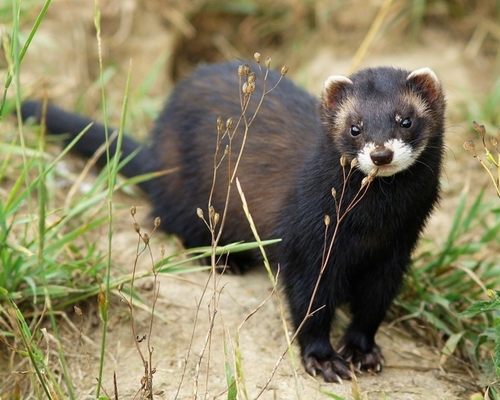
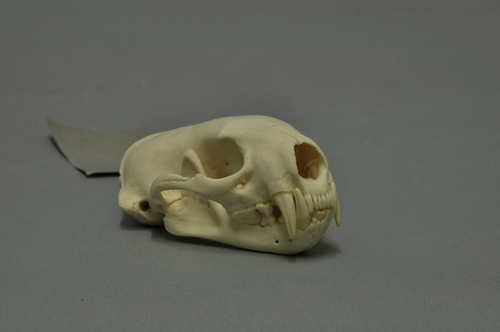
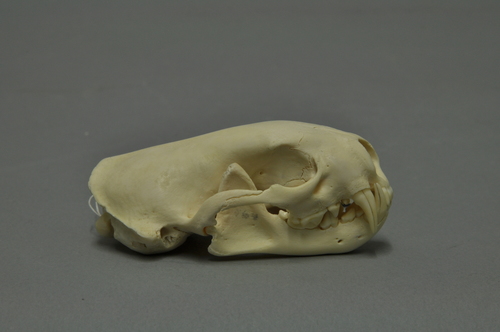
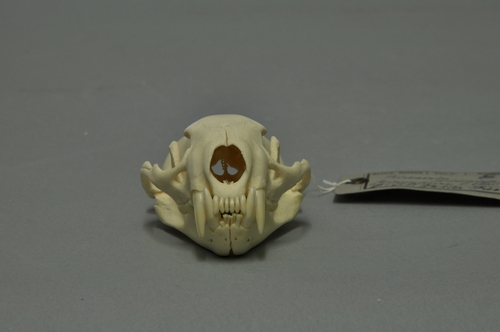
The appearance of the European polecat is typical of members of the genusMustela, though it is generally more compact in conformation and, although short-legged, has a less elongated body than the European mink or steppe polecat. The tail is short, about ⅓ its body length. The eyes are small, with dark brown irises. The hind toes are long and partially webbed, with weakly curved 4 mm-long, nonretractable claws. The front claws are strongly curved, partially retractable, and measure 6 mm in length. The feet are moderately long and more robust than in other members of the genus. The polecat's skull is relatively coarse and massive, more so than the mink's, with a strong, but short and broad facial region and strongly developed projections. In comparison to other similarly sized mustelids, the polecat's teeth are very strong, large and massive in relation to skull size. Sexual dimorphism in the skull is apparent in the lighter, narrower skull of the female, which also has weaker projections. The polecat's running gait is not as complex and twisting as that of the mink or stoat, and it is not as fast as the mountain weasel (solongoi), stoat or least weasel, as it can be outrun by a conditioned man. Its sensory organs are well developed, though it is unable to distinguish between colours.
The dimensions of the European polecat vary greatly. The species does not conform to Bergmann's rule, with the pattern of size variation seeming to follow a trend of size increase along an east-west axis. Males measure 350–460 mm in body length and females are 290–394 mm. The tail measures 115–167 mm in males and 84–150 mm in females. Adult males in middle Europe weigh 1,000-1,500 grams and females 650-815 grams. Gigantism is known among polecats, but specimens exhibiting this are likely the products of polecat-mink hybridisation.
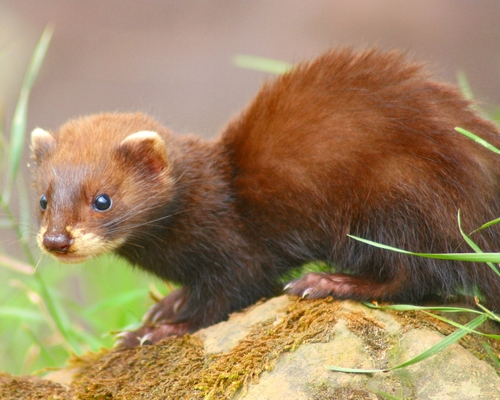
The winter fur of the European polecat is brownish black or blackish brown, the intensity of which is determined by the colour of the long guard hairs. On the back and flanks, the dark tone is brightened by bright whitish-yellowish, sometimes yellowish-greyish underfur which shows through. The lightly coloured underfur is not equally visible on different parts of the body. On the back and hindquarters, the underfur is almost completely covered by the dark guard hairs. On the flanks, though, the lightening is well defined, and contrasts sharply with the general tone of the back. The throat, lower neck, chest and abdomen are black or blackish brown. The limbs are pure black or black with brown tints, while the tail is black or blackish brown, completely lacking light underfur. The area around and between the eyes is black-brown, with a longitudinal stripe of similar colour along the top of the nose. The ears are dark brown and edged with white. The summer fur is short, sparse and coarse. It is greyer, duller and lacking in the lustre of the winter fur. The underfur is more weakly developed in the summer fur, and has a brownish-grey or rusty-grey colour. The polecat is a good swimmer, but its fur is not as well insulated against cold water as the American mink's; while a mink will take 118 minutes to cool in a water temperature of 8 °C, the polecat cools down much faster at 26–28 minutes.
Polecats were found in two major phenotypes a typic one and a dark fur one with no black mask. Colour mutations include albinos and erythrists. In typical erythristic individuals, the underfur is usually bright reddish. The guard hairs on the trunk are bright reddish or reddish brown. Black guard hairs are absent on the lower body and head. In some rare cases, the guard hairs are so light, they are almost indistinguishable from the pale-yellow underfur. In these cases, the whole animal is a very light golden-yellow colour.
Sources and Credits
- (c) Aleksandar, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), uploaded by Aleksandar
- (c) Klaus Rassinger, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mustela_putorius_03_MWNH_464.jpg
- (c) Klaus Rassinger, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mustela_putorius_02_MWNH_464.jpg
- (c) Klaus Rassinger, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mustela_putorius_01_MWNH_464.jpg
- (c) Wikipedia, some rights reserved (CC BY-SA), http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_polecat
More Info
iNat Map
| Region | Banat, Bačka, Južno Pomoravlje, Kosovo i Metohija, Podrinje i Posavina, Rasina i Toplica, Raška, Srem, Timok i Braničevo, Šopluk, Šumadija |
|---|